The new 2023 OT Cyber Threats Report is available – a collaboration between Waterfall Security Solutions and ICSSTRIVE. The collaboration reports on credible public disclosures of cyber attacks with physical consequences in discrete manufacturing and process industries world-wide during 2022.
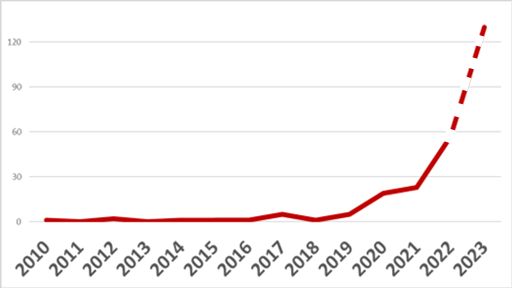
The report also looks at all such cyber attacks since 2010. The report concludes that in the decade 2010-2019, OT cyber threats were a largely theoretical problem. In the current decade however, the problem has become very real and these kinds of attacks are more than doubling annually at exponential growth (see Figure 1). At the current rate, we should expect cyber attacks in 2027 to cause shut-downs or other physical consequences in over 15,000 industrial sites, world-wide.
OT Cyber Threats: Major Findings
Ransomware is responsible for most attacks in the report, shutting down physical operations all over the world. These attacks brought about not just physical shutdowns but also financial losses. Some of 2022’s highest-profile incidents include:
- Outages at well-known car, tire and food & beverage brands and manufacturers,
- Flight cancellations and delays for tens of thousands of air travellers in four separate attacks,
- Physical operations impacted in four attacks on metals and mining, with one of the attacks resulting in a fire and material equipment damage,
- Malfunctions of loading and unloading of cargo containers, fuel, and bulk oil for half a dozen seaports on three continents, and
- Two of these attacks cited as a significant factor in the bankruptcy of two victim organizations.
The report observes that the most sophisticated ransomware criminal groups are today using attack tools and techniques that were the sole domain of nation-state adversaries less than 5 years ago. The report cites the latest US Administration’s Cybersecurity Strategy report as confirming that nation-state-grade attack tools are now available to purchase by other nation states and criminal actors.
The remaining 10% of attacks in the report were due to hacktivists – “amateur” attackers with a political agenda. All of the year’s hacktivist attacks with physical consequences were associated with two on-going physical conflicts: the Israel / Iran conflict and the Ukraine / Russia conflict.
Good News
The report also highlights defensive developments in the year 2022. The biggest such development was the publication the US Department of Energy’s Cyber-Informed Engineering Strategy. The strategy lays out a plan to gather into one body of knowledge: safety engineering, network engineering and other engineering techniques for mitigating threats to public safety and to physical operations due to cyber threats. These types of techniques are unique to the OT space – these techniques are not represented at all in IT-centric standard such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, nor are they represented in even many OT-centric cybersecurity standards such as the widely referenced IEC 62443 standard.
Bottom Line
The joint Waterfall and ICSSTRIVE OT cyber threats report covers year-on-year attack trends to see where we are headed in the global cyber threat environment. To the greatest extent practical, the team behind the report has gathered as much data as available to track the number and frequency of these cyber events – an Appendix to the report for example, contains a complete list of such events in the public record since 2010, with links to public reports of the attacks.
The report also covers important defensive developments, including the CIE, as well as developments in artificial intelligence and global standards and guidelines.
